The convergence of data analytics and sustainability is a promising development for logistics and supply chains. In this blog, we explore this fascinating synergy, including how data analytics is shaping the future of sustainability.
1. Introduction
In a world teetering on the brink of environmental crisis, where cries of climate change grow ever louder, the transportation and logistics industry finds itself at a crossroads. Recently, an unconventional protest unfolded in the heart of Washington, D.C., as climate activists glued their hands to the road in front of the White House. Their message was crystal clear: the time for environmental complacency is over.
The transportation sector is the most significant contributor to logistics emissions, accounting for about 75% of the total. – The International Chamber of Commerce
The logistics sector significantly impacts the environment due to the energy-intensive nature of its operations, including transportation, warehousing, and distribution. As concerns about climate change and environmental sustainability grow, it’s becoming increasingly important for logistics companies to adopt sustainability and contribute to a greener future.
2. Why Sustainability Matters in Logistics?
Reducing carbon footprints is one of the most significant challenges facing the logistics industry in terms of sustainability. Picture this: Traffic congestion, carbon emissions clogging the skies, and inefficient supply chains guzzling fossil fuels. These are the grim realities that logistics companies face. But the good news is that sustainability offers the ultimate escape route.
Between 2022 and 2030, the global green technology and sustainability market is forecast to grow from 13.76 billion dollars to almost 62 billion U.S. dollars, increasing at a compound annual growth rate of 20.8%. – Statista
By electrifying fleets, optimizing routes, and reducing waste, we’re not just saving the planet but boosting efficiency and cutting costs. Sustainability is the GPS guiding us toward a cleaner, greener, and more profitable future in transportation and logistics. Sustainable logistics practices can also help businesses meet environmental regulations and avoid fines and penalties associated with non-compliance.
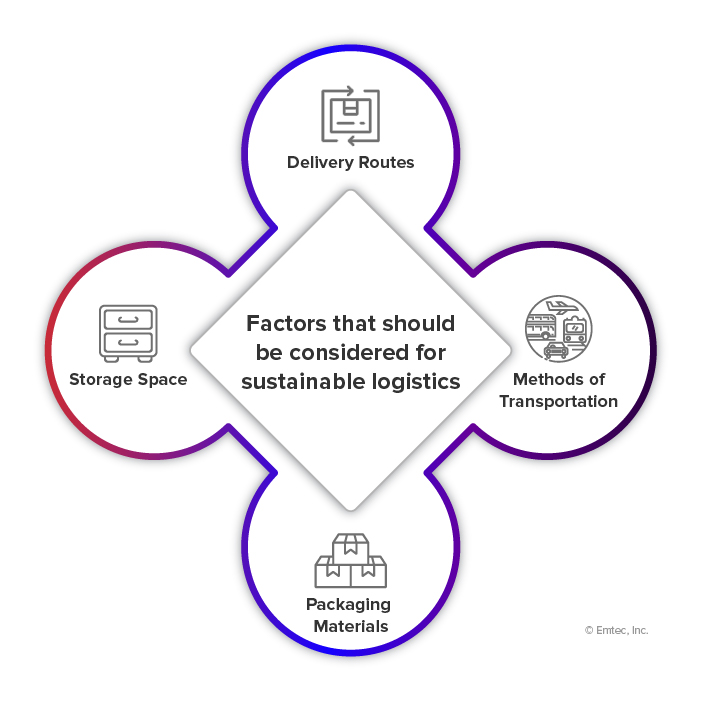
3. Sustainability Challenges in Transportation and Logistics
3.1 Environmental Challenges
The environmental impact of transportation is a pressing challenge within the logistics industry. This sector is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, air pollutants, and noise pollution. Trucks, ships, planes, and trains that transport goods and people emit carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter, which have detrimental effects on air quality and contribute to global warming.
According to Boston Consulting Group, transportation activities (aviation, rail, shipping, heavy and light trucking) account for 17% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
Data-driven sustainability initiatives are essential in mitigating the environmental impact of transportation and ensuring an eco-friendlier future. By analyzing vast amounts of data related to transportation operations, emissions, and environmental factors, companies can make informed decisions to reduce their carbon footprint.
3.2 Resource Consumption and Waste Generation
Resource consumption and waste generation are inherent challenges in the logistics industry. This sector relies heavily on fossil fuels for vehicles and equipment, leading to substantial resource depletion and greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the packaging materials used for shipping contribute to waste generation and environmental degradation, as they often end up in landfills or oceans.
To address these challenges, data analytics can be harnessed to optimize resource utilization and minimize waste. For instance, smart inventory management systems can help minimize overstocking and reduce waste associated with expired or unsold products.
4. Data’s Role in Attaining Sustainability in the Logistics Industry
Consider this scenario: You are evaluating switching fuel sources. You are considering electric energy or solar power or perhaps even an alternative fuel for your fleet including hydrogen fuel cells. These innovations are game changers for green logistics and transportation, zero carbon emissions, and making T&L more sustainable. But here’s the kicker – data is the fuel that powers these changes. Electric vehicles rely on data for efficient charging and range optimization. Solar-powered systems need data to predict energy generation and usage. And when it comes to alternative fuels like hydrogen, data helps us understand the best applications and infrastructure requirements.
So, while these green technologies can provide sustainability benefits, data is the unsung hero that ensures they’re utilized to their full potential in making the T&L industry greener and more sustainable. It’s not just about adopting new tech; it’s about using data to make them work smarter and cleaner.
5. Sustainable Initiatives to Reduce Carbon Footprints in Logistics Industry
Measuring and reducing carbon footprints is a fundamental sustainable practice in T&L. To reduce footprint, companies first need to comprehensively assess the carbon emissions associated with their operations. This includes emissions from vehicle fleets, energy consumption, and supply chain activities. Once a baseline is established, businesses can then set targets to reduce emissions. Regular monitoring and reporting of carbon emissions are crucial. By transparently tracking progress and sharing results with stakeholders, logistics companies can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and inspire others in the industry to follow suit. To achieve carbon reduction goals, companies can implement various strategies. Here are some sustainable initiatives and practices that can help achieve this goal:
5.1 Green Transportation
Green transportation represents a fundamental shift in how we move goods, acknowledging the urgent need to reduce the carbon footprint. Have a look at some best practices:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Transitioning to electric trucks, vans, and delivery vehicles can significantly reduce carbon emissions. Companies like Tesla and Rivian have been developing electric trucks for logistics.
A 2022 report by the Carbon Trust found that the logistics industry could reduce its greenhouse gas emissions by 20% by 2030 by adopting sustainable transportation practices.
- Hybrid Vehicles: In cases where EVs are not yet practical, hybrid vehicles can be a greener alternative, combining internal combustion engines with electric propulsion.
- Biofuels: Using biofuels, such as biodiesel or biogas, can reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These fuels can be produced from organic waste materials.
- Hydrogen: Hydrogen fuel-cell vehicles are becoming more viable for long-haul trucking and can be a zero-emission option when produced using renewable energy.
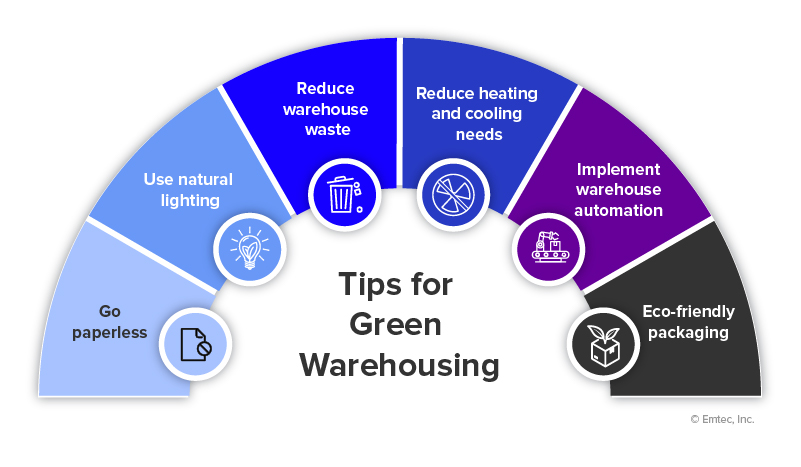
5.2 Green Warehouse (Material Handling)
In global supply chains, warehouses produce environmental pollution, mostly from heating, cooling, and lighting. Generally, the bigger the warehouse, the larger the carbon footprint. Efficient and sustainable material handling practices can lead to significant environmental benefits by minimizing waste, energy consumption, and emissions. Adopting high-density storage systems, recycling materials, and practicing just-in-time inventory management can also contribute to more sustainable warehouse operations.
A 2023 survey by the World Economic Forum found that 60% of logistics companies are investing in material handling green initiatives.
5.3 Waste Management
Effective waste management strategies play a vital role in reducing environmental impact in the logistics sector. Let’s have a look at some of those:
- Recycling Programs: Establish robust recycling programs within warehouses to ensure that materials like cardboard, plastic, and metal are recycled properly. Set recycling targets and monitor progress.
A 2023 survey by the Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals found that 85% of logistics companies have a waste reduction program in place.
- Composting: Implement composting programs for organic waste generated in the warehouse, such as food scraps or plant materials. Composting reduces the volume of waste sent to landfills.
- Reuse and Repurpose: Identify opportunities to reuse or repurpose materials within the logistics process. Otherwise, include reusing packaging materials or finding alternative uses for items that would be discarded.
- Electronic Documentation: Transition from paper-based documentation to electronic systems whenever possible. This reduces the consumption of paper and ink, leading to less waste.
- Waste Audits: Conduct regular waste audits to analyze the types and quantities of waste being generated. Use this data to identify areas for improvement and set waste reduction goals.
5.3 Waste Management
Logistics firms can significantly reduce their carbon footprint by adopting sustainable packaging practices. This includes using biodegradable or recyclable materials and reusable packaging solutions that minimize wastage and curb costs in the long run. By prioritizing sustainable packaging, companies can contribute to the global movement toward environmental conservation while improving their business operations and bottom line. Using lighter packaging is also a great idea for companies to adapt. This strategy reduces the weight of shipments thereby improving fuel efficiency, which equals lower carbon emissions.
According to Forbes, shipping containers dispatched from Asian manufacturers to the United States are, on average, 24% empty, and 25% of shipped goods consist of empty space.
There is considerable scope for enhancing packaging efficiency by addressing the issue of empty space. The greater the amount of empty space in a package, the more superfluous space it occupies during transportation, which inevitably leads to increased carbon emissions.
6. Data-Driven Sustainability: Charting the Course to a Greener Future
Driving sustainability in the transportation industry is crucial for mitigating climate change. Data-driven insights can guide logistics companies toward green logistics and transportation in several ways:
| Route Optimization: | Data analytics can optimize routes to:
|
| Vehicle Selection: | Data can be used to:
|
| Maintenance: | Predictive maintenance systems utilize:
|
| Fleet Management: | For organizations with large vehicle fleets:
|
| Demand Forecasting: | Data analytics can:
|
| Load Balancing: | Data can:
|
| Containers Capacity Mapping: | Partially loaded containers can contribute to increased carbon emissions in the transportation industry.
Data analytics can:
|
7. Use Cases: Data-Driven Sustainability Initiatives
Data-driven sustainability initiatives demonstrate their transformative potential in addressing environmental challenges and leading organizations toward a more sustainable future. Have a look at these use cases for better understanding.


8. Sailing Smoothly: Shippers’ Ideal Carrier Partnerships
As a shipper, you must be deeply committed to enhancing sustainability within your logistics operations. By using a data-driven approach, you can reduce pollution, ensure zero carbon emissions, and improve sustainability.
Also, to make transportation more sustainable and mitigate its contribution to climate change, the active participation of all stakeholders is necessary. In this regard, logistics carriers have a major role to play, and this requires a comprehensive understanding of the problem and visibility into the environmental impact of their shipments.
Nearly 40% of businesses struggle to identify and reach ESG targets to improve supply chain sustainability, and 20% of businesses are entirely clueless about improving supply chain sustainability. – EY
Logistics carriers are responsible for transporting goods from one place to another, and their decisions can significantly impact the environment. Imagine being able to optimize your shipping routes to reduce fuel consumption and emissions, identify opportunities for modal shifts to more eco-friendly transportation modes, and better manage your inventory to minimize waste. Data holds the key to making informed decisions, which helps logistics companies drive high-impact results.
Moreover, by integrating data analytics into your logistics operations, as a carrier, you can demonstrate your proactive commitment to sustainable practices, thereby positioning your partnership with shippers as a responsible and forward-thinking entity in the logistics realm.
For example, data analytics can be used to:
- Track and measure carbon emissions
- Identify opportunities for efficiency gains
- Develop new sustainability initiatives
- Evaluate the effectiveness of sustainability programs
When we achieve these sustainability milestones with the help of data analytics, it is a testament to collective efforts. Together in partnership, shippers and carriers can optimize logistics and contribute significantly to a more sustainable future.
9. Bridgenext: Your Beacon to Sustainable Logistics
An effective sustainability strategy is integral to T&L firm’s core corporate strategy. It should be deeply ingrained across the organization, and systematically executed. Our team of transport and logistics, and data experts collaborate closely with our client’s sustainability specialists and SMEs, ensuring industry, domain, and sustainability expertise are seamlessly integrated into sustainability planning. We take a holistic approach to sustainability, leveraging your internal resources, our experts, and stakeholders from our extensive global network to craft a comprehensive and enduring sustainability strategy.
Contact us today to transform your company into a champion of sustainability through the power of data!
References
www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/the-2023-cscmp-state-of-logistics-report-indicates-supply-chains-have-adapted-to-drive-resilience-after-two-years-of-global-volatility-301854268.html
www.freightwaves.com/news/make-last-mile-logistics-more-sustainable-with-3-key-initiatives
www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/green-technology-and-sustainability-market-102221
www.ey.com/en_gl/supply-chain/supply-chain-sustainability-2022